ON Grid Solar Rooftop System
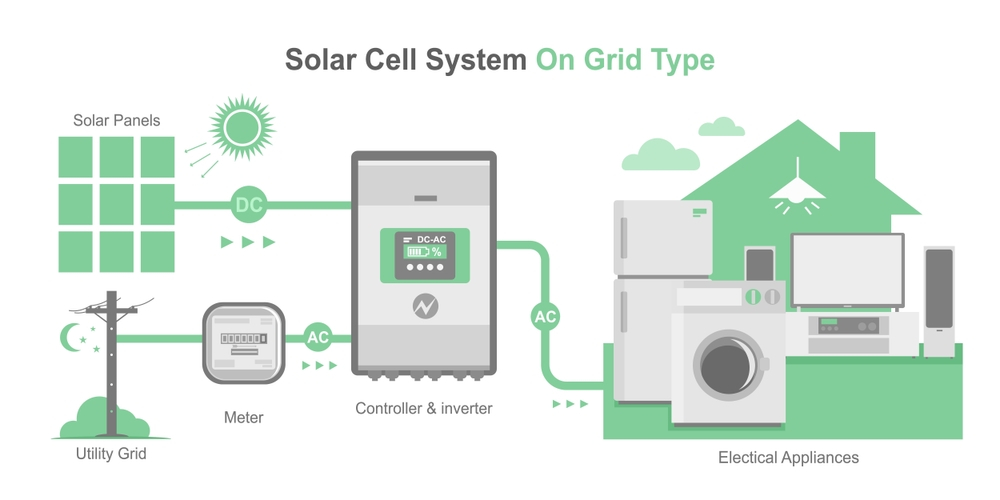
A specific kind of on-grid solar panel system that is intended to be installed on a building’s rooftop is known as an on-grid solar rooftop system. This kind of solar panel system may produce electricity from the sun’s energy to power your home or place of business because it is wired into the electrical grid.
Solar panels, an inverter, and a metre are commonly included in an on-grid solar rooftop system. The building’s rooftop is where the solar panels are situated, and they use sunshine to generate DC electricity. The DC electricity is then changed into AC electricity by the inverter, which may be utilised to power gadgets and appliances in your house or place of business.
How It Works?
An on-grid solar panel system, also known as a grid-tied solar system, is a photovoltaic (PV) system that generates electricity from the sun and feeds it into the utility grid. Here’s how it works:
Solar panels: The solar panel array is installed on the rooftop or in an open area with maximum exposure to sunlight. The panels are made up of multiple solar cells that convert sunlight into direct current (DC)
electricity.
Inverter: The DC electricity generated by the solar panels is sent to an inverter. The inverter converts the DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is the type of electricity used by most household appliances and the utility grid.
It can either be kept in batteries for use later on in the day in an off-grid solar system.
fed into the grid (solar system on-grid). Based on the feed-in-tariff rates (a charge set by the government for the purchase of solar power produced by solar plants) in your area, your electricity bill is reduced for the amount of power you have sold to the power grid.
Benifts

Guaranteed 24*7 power supply
The consumer will always have access to power and will never experience a power outage thanks to the ability to use either solar power or the main power grid.

Opportunity to earn more
With the help of a net metre installed at your home, you may keep track of how many units you transferred to the power grid and receive a credit for that on your home electricity account. Customers view this as a wise decision and an additional source of income. In almost every state in the USA and even in India, net metering is now required.
More Savings
The main reason to install an on-grid solar system is to save money on your electricity bill. To avoid paying peak demand costs, you might adjust your use during high demand periods. These are the higher fees that the utility charges for grid access during periods of high demand. You can also generate more money and reduce your electricity expenditures by implementing net metering.

Good Investment Returns
A grid-connected solar system is a great financial option. It has a five-year payback period and provides twenty years of free electricity. With solar energy, you can generate revenue from your property in as little as 4-5 years.

Works efficiently
The on-grid system collaborates with the grid. You can utilise the grid-tied solar system to power any home appliance; there are no limitations. It also makes use of all the solar energy produced by solar panels. For instance, a 1 kW on-grid system may deliver 5 kW of power.
Easy to Install
Installing an on-grid system on a rooftop is easy and may be done by oneself. On a variety of rooftops, including those of residences, office buildings, housing cooperatives, community centres, governmental organisations, for-profit companies, etc., it is simple to install.

Less Costly
An on-grid solar system is less expensive to build than an off-grid system because batteries are not required. It is less expensive when compared to other solar systems.
Less Maintenance
An on-grid solar system often requires less maintenance and lasts longer than an off-grid one.
Subsidies and Other Incentives
A user may benefit from government subsidies and other incentives to install on-grid solar systems.
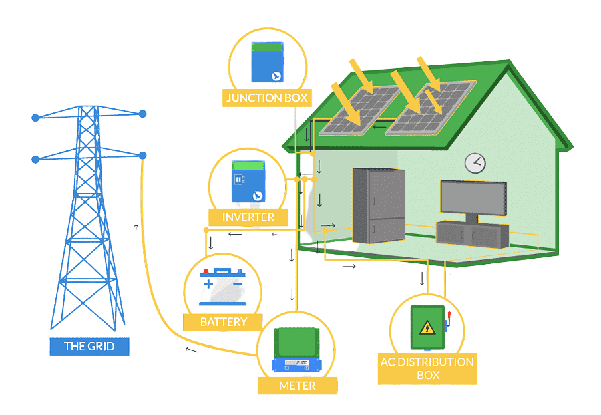
Primary Components
Solar Panel
Solar panels make up the majority of the on-grid solar system. They make up the majority of the cost of a solar system and are responsible for converting solar energy into electrical energy.
Safety Equipment
To shield the solar system from defects like lightning and other conditions, defence measures are used. Surge arrestors, breakers, grounding procedures, etc. are a few of them.
Lighting Arrestor
A lightning arrestor is used to stop lightning from striking the on-grid solar system.
Installation Accessories
These include installation-related materials including wires, cabling, mounting frameworks, junction boxes, etc.
Earthing Kit
An earthing kit protects the on-grid solar system against thunderstorms.
Solar Inverter
Solar inverters are used to convert the DC output from the solar panel into an AC supply.
Solar Wire
Solar wire or solar cable is used to transport electricity from the solar panels to the inverter. Most wires on the market fall into one of two categories, such as AC wire or DC wire. It is called a solar wire since the solar panel's output is DC current.
DCDB / ACDB
A DC Distribution Board (DCDB) is used to connect the output power from a solar panel to the input of the inverter, whereas an AC Distribution Board (ACDB) is used to transport electrical power from a solar inverter to an AC load system through an energy metre.
Net Meter & Solar Meter
Small, renewable energy-generating units can be connected to the power grid by utilities and their customers thanks to a specific metering and billing system called net metering. It is an essential component of an on-grid solar system because it keeps the reading required to request credit on your subsequent electricity bills. Net metering is especially important for solar energy because, unlike other renewable energy sources, solar energy is produced in huge amounts in the residential and commercial sectors.
Panel Stand
Panel supports are yet another crucial component of the entire solar system. Some people attempt to save some money by using a cheap stand without giving any thought to this element. However, keep in mind that this stand will hold the solar panels; as a result, if the stand is not sturdy, your solar panels may simply fall, resulting in a big loss. The skeletal framework is keeping the panel in place. These stands are frequently made of aluminium or galvanised iron. There are either fixed or portable solar panel stands that move with the sun.
CONTACT
- 10/3, Block 10, Sector 3, Rajendra Nagar, Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh 201005
- +91 7291047370, +91 9643834886
- info@amfareservices.in
